
Image: Googleimages; TS Service Team
Ankle injury accounts for 14%-21% of all sports injuries, and the incidence of basketball and football is as high as 40% and 25%. During running, the ankle is a key part of stress transmission. It can withstand three times the weight of the body. Therefore, if the ankle is weak, it will reduce the buffering capacity and efficiency, and increase the ankle joint and other parts (such as the knee joint). (Calf, calf) Risk of injury.
Ankle joint structure
The ankle joint is one of the more important joints in the body and one of the joints with complex structures. It is composed of the inferior tibial articular surface, the medial and lateral tibial articular surface, and the talus trochlear articular surface. Ligaments are reinforced on both sides of the joint. The lateral ligaments are more diffuse and weak, the muscles are also weak, and the lateral malleolus are low; the medial ligaments are more concentrated, thicker, wider, tougher, and higher in medial malleolus. Therefore, the ankle joint has poor stability and is easily injured.
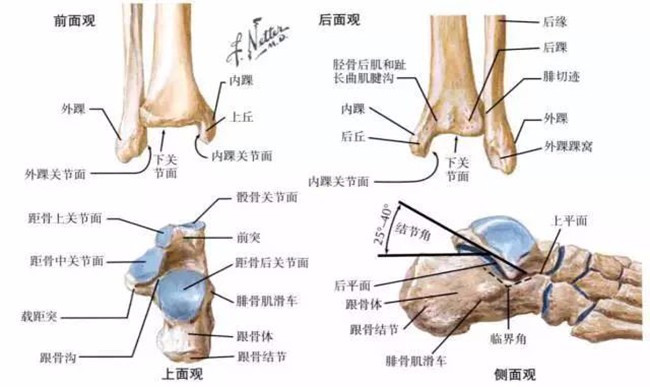
Ankle bony structure (Photo: Knight's orthopaedic color map)

Ankle ligament structure (Photo: Knight's orthopaedic color map)
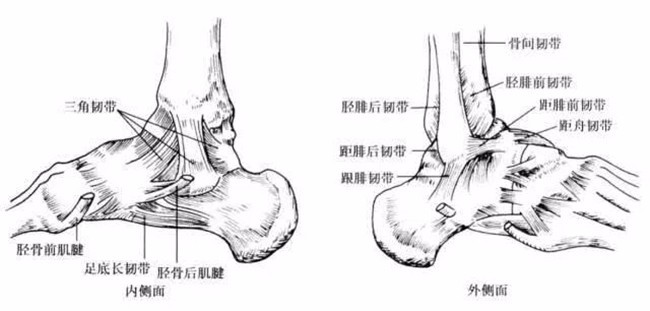
Ankle ligament structure 1 (Photo: Knight's orthopaedic color map)
The mechanism of ankle sprain
Injury mechanism: Most ankle sprains are caused by ankle inversion, and varus stress causes lateral collateral ligament tear. Usually seldom occur in the movement of valgus injury, more common in some serious external forces such as a car accident, valgus injury is usually more serious consequences, prone to dislocation of the ankle, fracture, medial ankle ligament tear, and even vascular nerve Damage is not discussed here for the time being. According to the degree of damage, it can be roughly divided into three degrees.
The degree I manifested as mild pain, slight incomplete tear of the lateral collateral ligament, slight swelling of the external malleolus, and rarely joint instability;
The degree II manifested as: moderate to severe pain, accompanied by swelling, stiffness and difficulty walking, visible part of the foot ecchymosis, moderate incomplete tear of the lateral collateral ligament, may be associated with partial joint instability;
III degree performance: the most serious injury, pain and swelling are often more obvious, often obvious mottled plantar feet, lateral collateral ligament completely torn, joint instability appears to affect the normal activities. Of course, if it is seriously accompanied by anterior visceral impingement, fracture of the lateral malleolus, and even dislocation of the sacroiliac joint.
1. Different types of ankle sprains and ligament injuries

2. Ankle sprain clinical grading
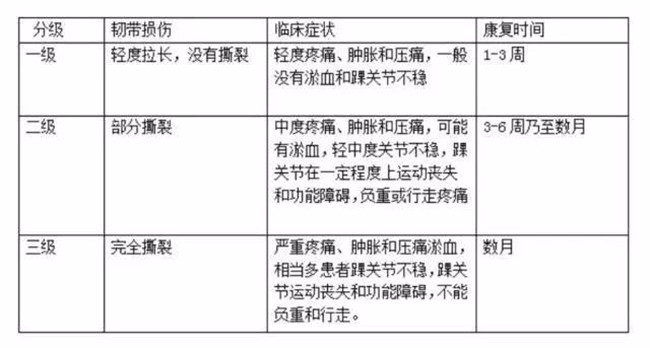

(Ankle sprain classification)
Treatment of ankle sprain
1. Emergency treatment:
The classic RICE principle for emergency handling of ankle sprains:
Rest: stop walking, rest the injured area, and reduce further damage;
Ice: Reduces the temperature of the injured area, reduces inflammation and muscle spasms, relieves pain and inhibits swelling. 10-20 minutes each time, more than 3 times a day, pay attention not to apply ice directly to the affected area, you can use a wet towel to wrap the ice, to avoid frostbite. Ice packs are limited to 48 hours after injury. Sprain within 48 hours should not: heat.
Compression: Use an elastic bandage to wrap the injured ankle joint and press it properly to reduce swelling. Be careful not to over pressurize, otherwise it will aggravate the swelling and ischemia of the far limb.
Elevation: Elevation of the limb above the heart, increasing venous and lymphatic drainage, reducing swelling, and promoting recovery.
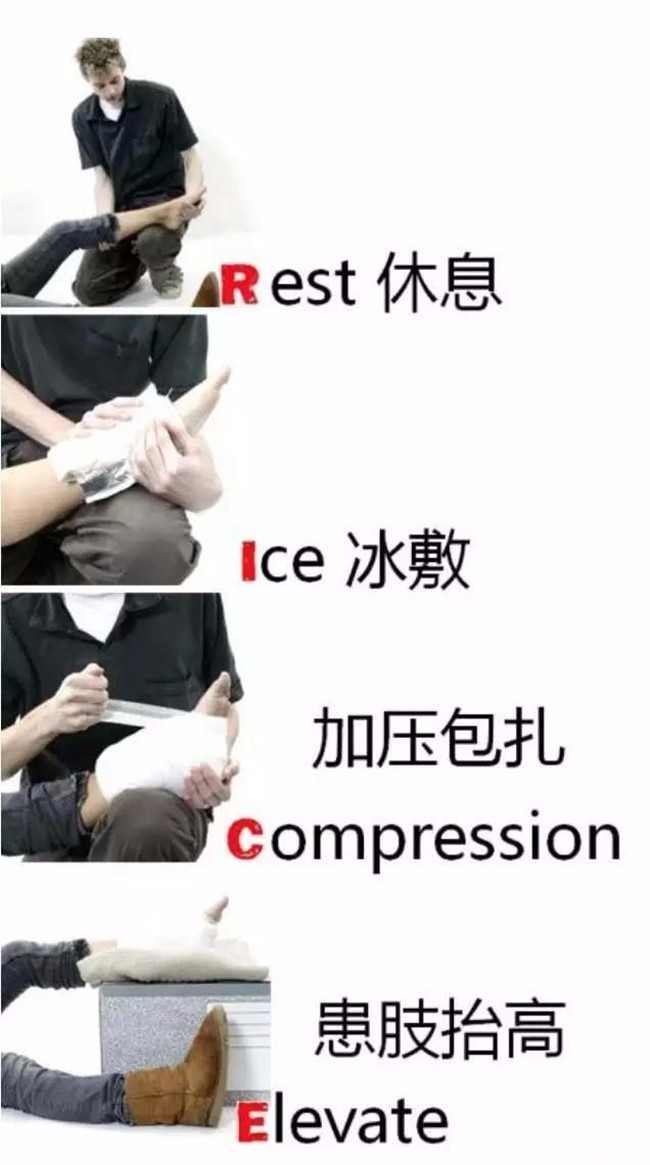
2. Follow-up treatment:
The treatment of the acute phase can use some physical therapy to control swelling and inflammation, and take anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs under the guidance of a doctor. Acute ankle sprains generally require braking and rest for at least 2 weeks. If soreness improves and there are no apparent exacerbations, some functional training can be performed to help improve joint mobility and further control swelling.
Plastering is a more effective and economical method of braking protection. However, gypsum is relatively hot and uncomfortable, it is difficult to wear and clean, and it cannot walk on the ground. The best fixed method at present is to choose the right brace and protective gear.
The recommended choice for the acute phase is the limited splint braces. Walking boots protection is usually in place, but also breathable, convenient walking activities and cleaning, but the price is more expensive, if the economic conditions allow the recommended selection.
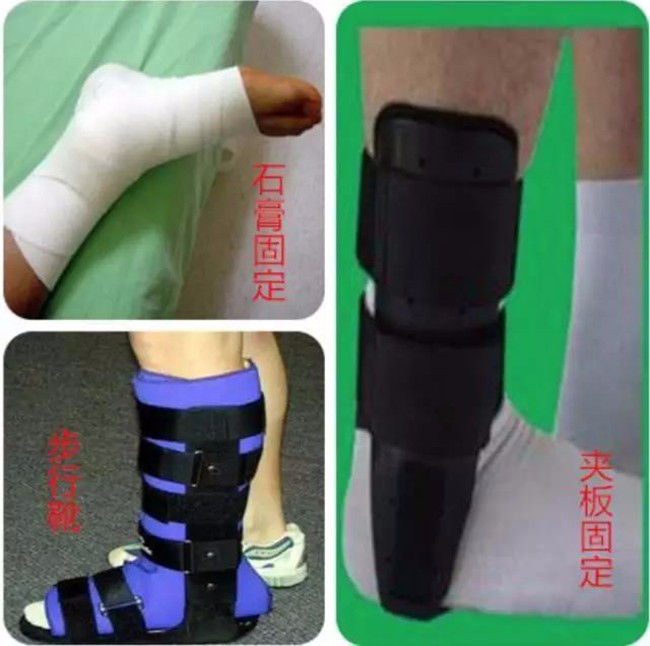
Ankle sprain brake method
After the acute period, doing stretching and strength training can help the affected limbs to restore activity and related muscle strength, and lay the FOUNDATION for normal walking and exercise. Before performing rehabilitative training, please ensure that your ankle sprain has basically recovered, that is, you can walk normally, do not bend without significant pain, before you can do strength training.
The fundamental purpose of ankle strength training is to improve the stability of the ankle joints, prevent sprains and even sprained ankles, and increase the strength of the ankle.
The principle of ankle rehabilitation training: long-term, increasing difficulty.
The difficulty of practice is gradually increasing and is roughly divided into:
1, small-scale sports - flexibility exercises
2, balance - perception exercises
3, strengthen strength exercises
4, strengthen the lasting practice
5, flexibility - enhanced exercises
Specific training methods:
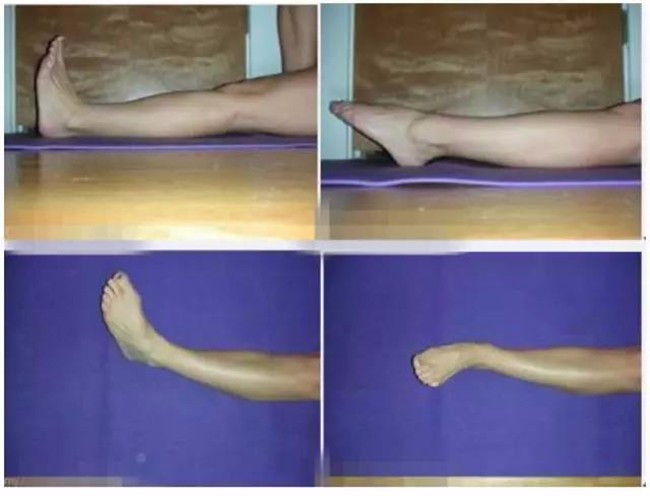
1, the initial small-scale flexibility exercises:
Ankle wrap exercise: Move the ankle to complete the entire range of movement (up and down, before and after, around the ring), to ensure that the leg does not move throughout the entire process, only to move the ankle, you can imagine writing, as shown:
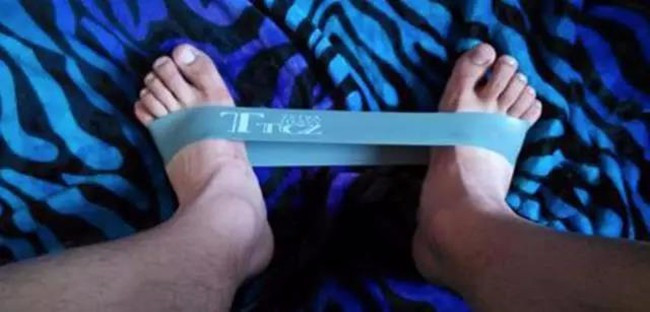
2. After half a month, use an ankle training belt for strength training.
Use ankle training with assistive strength training:
1) Anti-Resistance Eversion
On the bed or stool, use rubber bands to cover the two feet, and take the foot out with force and valgus. Repeat 15 times and rest for 30 seconds. Make 4-6 groups, 1-2 times a day.
2) Resistance to foot varus
The posture is equal to the anti-resistance foot valgus, the rubber band is fixed at the distal end (instrument or other), and the varus is forced inwards, the quantity and requirement are the same as that of the anti-resistance iliac valgus.

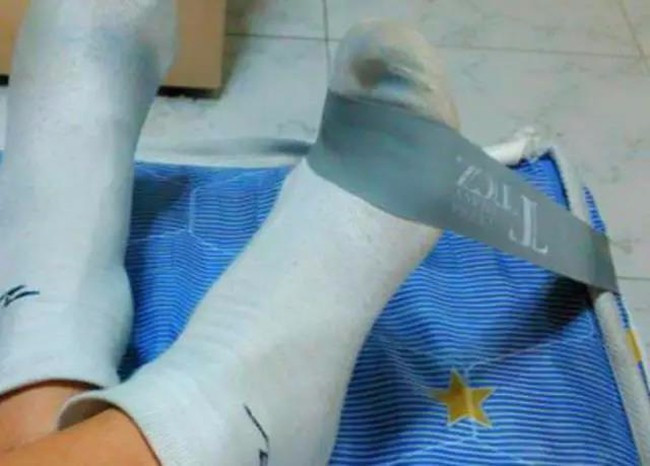
3) Resistant hook feet
With rubber band as resistance, the distal end is fixed (the site of the device is even using the foot of the bed), and it is put on the foot. Stretching from the straight position to the flexion position as hard as possible, pause for a minute (a pause of about one second), and slowly release it. Repeat 20 times, rest for 30 seconds, total 4-6 groups, 1-2 times a day;
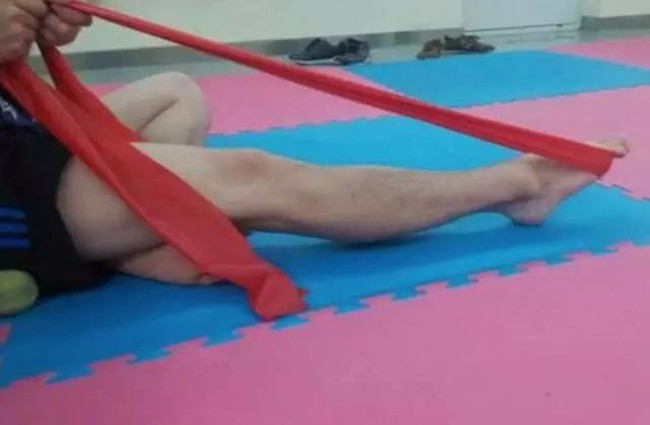
4) Resistance resistance
Use the ankle training band as a resistance, hold it proximally (hands), place it on the foot, stretch from the flexed position to the stretched position as far as possible, pause for a moment, slowly let go, repeat 20 times, rest for 30 seconds, total Do 4-6 groups, 1-2 times a day.

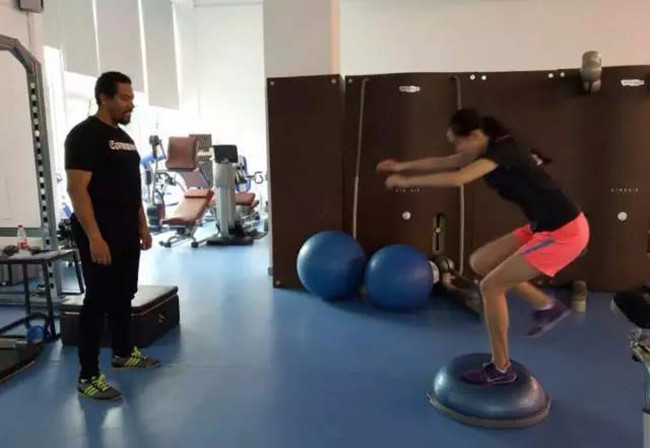
5) Balance Board Training
Standing on the balance board, use the power of one leg to control the balance of the body as much as possible, 15-20 revolutions each time, rest for 30 seconds, a total of 2-3 times per group, 1-2 groups per day.

(TS provides information on rehabilitation services for the Shanghai team)
Patients with a degree of ligament injury above III degree on MRI or B-mode ultrasound are required to prevent chronic ankle instability. It is usually recommended to follow up for 3 months on the basis of active rehabilitation training and conservative treatment, and then check the ligament stability and joint looseness. If the recovery is not obvious, and affects normal activities, or recurrent chronic instability, consider surgery.
Usually surgery can be combined with arthroscopic minimally invasive + small incision repair method. Many groups of ligament rupture, such as the anterior tibial and Achilles tendon ligament rupture at the same time, or the inferior tibial ligament rupture can also be used to transplant tendon reconstruction surgery.


(Ankle lateral collateral ligament reconstruction)
Precautions for ankle sprain
During the rehabilitation process, if there are some of the following situations, you need to go to the hospital in time to avoid delays:
1. The swelling after acute sprain is very obvious, with a large number of skin bruises, with marked tenderness and limited activity;
2. Swelling pain slowly subsides after a break in the brakes, but there are painful walking activities for a long time, with swelling of the joints (easily occurring on uneven ground or stairs);
3. Swelling and pain improved, but normal walking or exercise often appears to "play soft legs" and may be accompanied by falls and other unstable symptoms;
4. There was a history of an ankle sprain, a sprain in the movement, and a history of repeated sprains or loose joint instability;
5. There is secondary redness, fever, and pain throughout the foot and it may develop into chronic pain or complex local pain syndrome (CRPS).
Cheek Powder,Flawless Liquid Foundation,Baby Cream Foundation,Cream Blush
Guangzhou believe cosmetics co.,ltd , https://www.believecosmetics2010.com